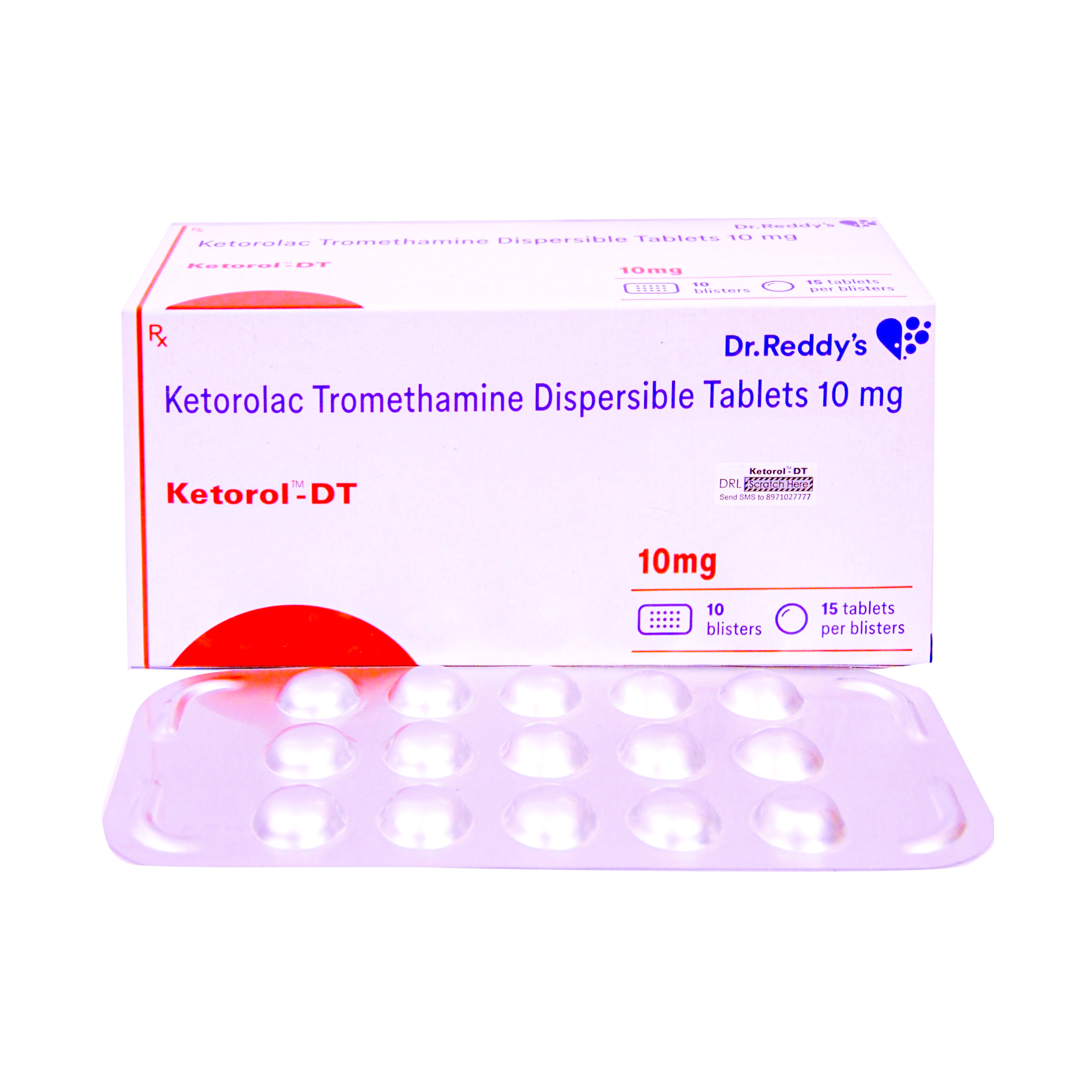
KETOROL DT (Toradol)10mg – 150 tablet
Each ketorol Contains 10 mg Ketorolac Trometamol 150 tablets. Used in the short-term management of moderate to severe pain
ATC Classification: M01AB15
Active Ingrediant: Ketorolac Trometamol
Generic Name: KETOROL DT
Manufacturer: Dr.Reddy Lab
Strength: 10mg
Dosage Type: Tablet
Packaging Type: Foil in Box
Contains: 150 Tab
Ketorolac Information
What is this drug used for?
• It is used to ease pain.
Possible side effects
Ketorolac may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:
• Headache.
• Stomach pain or heartburn.
• Upset stomach.
Some side effects can be serious. If you experience any of these symptoms, call your doctor immediately or get emergency medical treatment:
• Signs of an allergic reaction, like rash; hives; itching; red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin with or without fever; wheezing; tightness in the chest or throat; trouble breathing, swallowing, or talking; unusual hoarseness; or swelling of the mouth, face, lips, tongue, or throat.
• Signs of bleeding like throwing up or coughing up blood; vomit that looks like coffee grounds; blood in the urine; black, red, or tarry stools; bleeding from the gums; abnormal vaginal bleeding; bruises without a cause or that get bigger; or bleeding you cannot stop.
• Signs of kidney problems like unable to pass urine, change in how much urine is passed, blood in the urine, or a big weight gain.
• Signs of high potassium levels like a heartbeat that does not feel normal; feeling confused; feeling weak, lightheaded, or dizzy; feeling like passing out; numbness or tingling; or shortness of breath.
• Signs of high blood pressure like very bad headache or dizziness, passing out, or change in eyesight.
• Chest pain or pressure.
• Weakness on 1 side of the body, trouble speaking or thinking, change in balance, drooping on one side of the face, or blurred eyesight.
• Shortness of breath, a big weight gain, or swelling in the arms or legs.
• Feeling very tired or weak.
• A very bad skin reaction (Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis) may happen. It can cause very bad health problems that may not go away, and sometimes death. Get medical help right away if you have signs like red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin (with or without fever); red or irritated eyes; or sores in your mouth, throat, nose, or eyes.
• Liver problems have happened with drugs like this one. Sometimes, this has been deadly. Call your doctor right away if you have signs of liver problems like dark urine, feeling tired, not hungry, upset stomach or stomach pain, light-colored stools, throwing up, or yellow skin or eyes.
Medication Safety Issues
Sound-alike/look-alike issues:
Ketorolac may be confused with Ketalar, methadone
Toradol may be confused with Foradil, Inderal, TEGretol, traMADol, tromethamine
Storage/Stability
Injection: Store at 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Protect from light. Injection is clear and has a slight yellow color. Precipitation may occur at relatively low pH values.
Tablet: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Protect from light and excessive humidity.
Adverse Reactions
Frequencies noted for parenteral administration:
>10%:
Central nervous system: Headache (17%)
Gastrointestinal: Gastrointestinal pain (13%), dyspepsia (12%), nausea (12%)
>1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Edema (4%), hypertension
Central nervous system: Dizziness (7%), drowsiness (6%)
Dermatologic: Diaphoresis, pruritus, skin rash
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea (7%), constipation, flatulence, gastrointestinal fullness, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, gastrointestinal perforation, gastrointestinal ulcer, heartburn, stomatitis, vomiting
Hematologic & oncologic: Anemia, prolonged bleeding time, purpura
Hepatic: Increased liver enzymes
Local: Pain at injection site (2%)
Otic: Tinnitus
Renal: Renal function abnormality
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Abnormality in thinking, acute pancreatitis, acute renal failure, agranulocytosis, alopecia, anaphylactoid reaction, anaphylaxis, angioedema, anxiety, aplastic anemia, aseptic meningitis, asthma, azotemia, blurred vision, bradycardia, bronchospasm, bruise, cardiac arrhythmia, cardiac failure, chest pain, cholestatic jaundice, coma, confusion, conjunctivitis, cough, cystitis, depression, dyspnea, dysuria, eosinophilia, epistaxis, eructation, erythema multiforme, esophagitis, euphoria, exacerbation of urinary frequency, exfoliative dermatitis, extrapyramidal reaction, fever, flank pain, flushing, gastritis, glossitis, hallucination, hearing loss, hematemesis, hematuria, hemolytic anemia, hemolytic-uremic syndrome, hepatic failure, hepatitis, hepatotoxicity (idiosyncratic) (Chalasani, 2014), hyperglycemia, hyperkalemia, hyperkinesis, hypersensitivity reaction, hyponatremia, hypotension, increased susceptibility to infection, increased thirst, infertility, inflammatory bowel disease, insomnia, interstitial nephritis, jaundice, lack of concentration, laryngeal edema, leukopenia, lymphadenopathy, maculopapular rash, melena, myocardial infarction, nephritis, nervousness, oliguria, pallor, palpitations, pancytopenia, paresthesia, pneumonia, polyuria, proteinuria, psychosis, pulmonary edema, rectal hemorrhage, renal failure, respiratory depression, rhinitis, seizure, sepsis, skin photosensitivity, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, stomatitis (ulcerative), stupor, syncope, tachycardia, thrombocytopenia, tongue edema, toxic epidermal necrolysis, tremor, urinary retention, urticaria, vasculitis, vertigo, weakness, weight gain, wound hemorrhage (postoperative), xerostomia